Exploring the Ancient Wisdom of Ayurveda A Comprehensive Guide.

Welcome to our journey through the fascinating world of Ayurveda, an ancient healing system with roots deep in the Indian subcontinent. In this article, we’ll delve into the etymology, principles, practice, and modern applications of Ayurveda, shedding light on its rich history, therapeutic techniques, and ongoing research.
Etymology:
The term “Ayurveda” originates from Sanskrit, where “Ayur” means life and “Veda” means knowledge or science. Together, Ayurveda translates to “the science of life,” reflecting its holistic approach to health and well-being.
Eight Components:
Ayurveda divides medicine into eight canonical components known as Ashtanga Ayurveda. These include internal medicine, surgery, ear-nose-throat (ENT) treatment, pediatrics, toxicology, rejuvenation therapy, aphrodisiacs, and psychiatry.
Principles and Terminology:
At the core of Ayurveda lie three elemental doshas: Vata (air and ether), Pitta (fire and water), and Kapha (earth and water). Balance among these doshas is essential for health, while imbalance leads to disease. Ayurvedic texts also describe the importance of proper diet, lifestyle, and seasonal routines in maintaining equilibrium.
Practice:
Ayurveda employs a variety of therapeutic modalities to restore balance and promote well-being. These include herbal medicine, dietary adjustments, meditation, yoga, massage, detoxification procedures (Panchakarma), and lifestyle recommendations tailored to individual constitution and imbalances.

Substances Used:
Ayurvedic preparations often include a wide array of natural substances, including herbs, minerals, metals, and animal products. These ingredients are combined to create complex formulations aimed at addressing specific health concerns and restoring harmony within the body.
Panchakarma:
Panchakarma is a cornerstone of Ayurvedic detoxification therapy, consisting of five cleansing procedures: Vamana (emesis), Virechana (purgation), Basti (enema), Nasya (nasal administration), and Raktamokshana (bloodletting). These procedures aim to eliminate toxins, rejuvenate tissues, and restore balance.
Current Status:
Ayurveda continues to thrive both within and outside the Indian subcontinent, with a growing global interest in its holistic approach to health and wellness. Ayurvedic clinics, spas, and retreats offer a range of treatments, while Ayurvedic products and supplements are increasingly popular worldwide.
Outside the Indian Subcontinent:
Ayurveda’s influence extends beyond its place of origin, with practitioners and enthusiasts around the world embracing its principles and practices. Ayurvedic centers and schools can be found in numerous countries, offering education, consultations, and treatments to a diverse clientele.
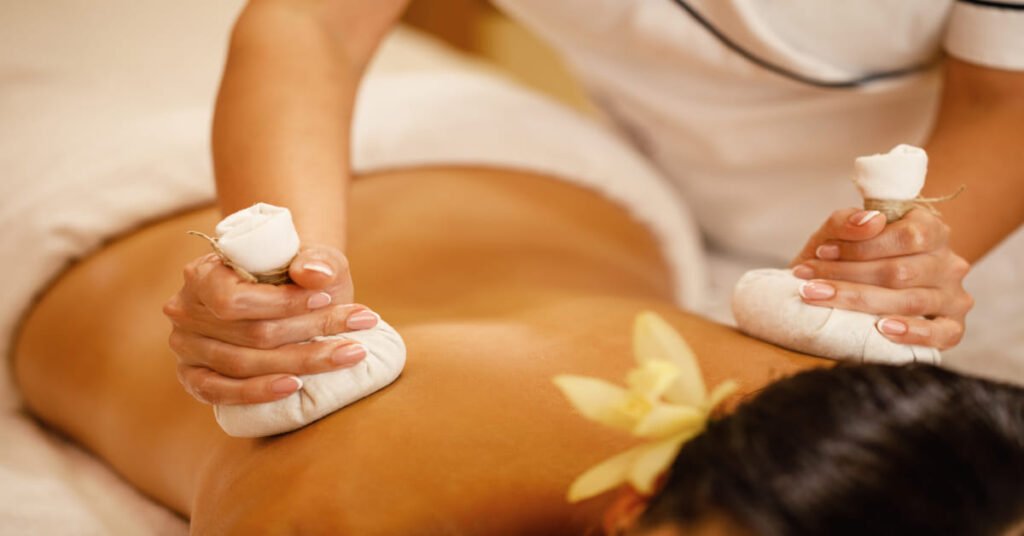

Classification and Efficacy:
While Ayurveda has been classified as pseudoscientific by some, its efficacy in promoting health and well-being is supported by centuries of tradition and ongoing research. Studies have explored Ayurvedic interventions for various conditions, with promising results in areas such as stress reduction, pain management, and digestive disorders.
Research:
Ongoing research seeks to further understand the mechanisms of action behind Ayurvedic therapies and validate their efficacy through rigorous scientific inquiry. Collaborations between Ayurvedic practitioners and modern researchers aim to bridge the gap between traditional wisdom and evidence-based medicine.
Use of Toxic Metals:
Concerns have been raised about the presence of toxic metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic in some Ayurvedic preparations. Quality control measures and regulatory standards are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of Ayurvedic products and protect public health.
History:
Ayurveda boasts a rich historical legacy dating back thousands of years, with ancient texts such as the Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita laying the foundation for its practice. Over centuries, Ayurveda has evolved and adapted to changing cultural and scientific landscapes, yet its core principles remain rooted in timeless wisdom.

Further Development and Spread:
As Ayurveda continues to evolve and spread globally, collaborations between traditional practitioners and modern healthcare systems offer new avenues for integration and innovation. By embracing its heritage while embracing modern advancements, Ayurveda holds the promise of a holistic approach to health that transcends borders and cultures.
References:
- Charaka Samhita: The Ayurvedic Classic. (n.d.). Retrieved from [source]
- Sushruta Samhita: Ancient Surgical Treatise. (n.d.). Retrieved from [source]
- Chopra, A., Saluja, M., Tillu, G., & Sarmukkaddam, S. (2019). Ayurveda-modern medicine interface: A critical appraisal of studies of Ayurvedic medicines to treat osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 10(1), 11–18. [source]
Ayurvedic Medicines Ancient Remedies for Modern Wellness
Ayurvedic medicines are traditional remedies that have been used for centuries in the practice of Ayurveda, a holistic healing system originating from India. These medicines are derived from natural sources such as herbs, minerals, metals, and animal products, and are prepared using traditional methods based on ancient Ayurvedic texts.
Philosophy and Principles:
The philosophy behind Ayurvedic medicines is rooted in the belief that balance is key to health, and imbalances in the body’s doshas (Vata, Pitta, and Kapha) can lead to illness. Ayurvedic treatments aim to restore this balance by addressing the root cause of the problem rather than just alleviating symptoms.
Types of Ayurvedic Medicines:
There is a wide variety of Ayurvedic medicines available, each formulated to target specific health issues or imbalances. Some common types of Ayurvedic medicines include:
- Herbal Formulations
- Rasayanas
- Ayurvedic Oils
- Ayurvedic Churnas
- Ayurvedic Syrups and Tonics
Famous Ayurvedic Products:
When it comes to famous Ayurvedic products, there are several well-known brands and formulations that have gained popularity both in India and around the world. Some of these include:
- Dabur Chyawanprash
- Himalaya Liv.52
- Patanjali Divya Swasari Ras
- Baidyanath Shankhpushpi Syrup
- Zandu Vigorex Capsules
While Ayurvedic medicines can be effective for certain health conditions, it’s always advisable to consult with a qualified Ayurvedic practitioner or healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen. Additionally, quality and safety standards vary among Ayurvedic products, so it’s essential to choose reputable brands and products with proper certification and quality assurance.

Navigating Through Time – Past, Present, and Future
Unveiling the Roots Ayurveda’s Journey Through History
Vedic Beginnings:
- Tracing Back: Ayurveda’s Genesis in Ancient Vedic Texts (Around 1500 BCE)
- Charaka and Sushruta: Pioneers of Ayurvedic Medicine
- Ayurvedic Principles in Ancient Indian Society
Golden Age of Ayurveda:
- Flourishing Traditions: Ayurveda’s Golden Era of Development
- Ayurvedic Schools and Centers of Learning
- Contributions to Medical Science and Philosophy
Modern Revival and Global Recognition:
Reviving the Tradition: Ayurveda’s Resurgence in the Modern World
Colonial Era and Revival Movements:
- Ayurveda in the Colonial Era: Challenges and Adaptations
- Revival Movements: Rekindling Interest in Traditional Healing
- Ayurveda’s Role in India’s Independence Movement
Global Spread and Recognition:
- Ayurveda Goes Global: From Ancient Tradition to Global Phenomenon
- Ayurveda in the West: Adoption, Adaptation, and Integration
- UNESCO Recognition: Safeguarding Ayurveda’s Cultural Heritage

Future Pathways and Potential: Navigating Forward: Ayurveda’s Trajectory in the 21st Century
Integrating Tradition with Innovation:
- Modern Applications: Integrating Ayurvedic Wisdom with Contemporary Science
- Ayurvedic Pharmaceuticals: Innovations in Formulations and Delivery
- Ayurveda and Sustainable Healthcare: A Model for the Future
Digital Age and Accessibility:
- Ayurveda in the Digital Era: Online Platforms for Wellness and Education
- Telemedicine and Remote Consultations: Bridging Gaps in Healthcare Access
- Ayurveda Apps and Wearable Technology: Personalized Wellness at Your Fingertips
Conclusion: Ayurveda: A Timeless Tradition, A Continuing Journey
In conclusion, Ayurveda offers a holistic approach to health and wellness that has stood the test of time. By integrating ancient wisdom with modern research and practice, Ayurveda continues to inspire healing and transformation on a global scale.